Hard SUP vs Inflatable Paddle Board Construction
So you're ready to get a paddle board for yourself. Do you want a hard SUP or an inflatable paddle board? We cover every aspect of both types of board construction.
Key Highlights
- Construction Differences: Hard SUPs are built from EPS foam and fiberglass for rigidity and performance, while inflatable SUPs utilize PVC and drop stitch technology for flexibility and portability.
- Durability and Performance: Durable hard boards are designed to withstand impacts, ideal for rough waters. Inflatable boards offer surprising rigidity and versatility, with advancements in materials enhancing their durability.
- Portability and Storage: Inflatable SUPs excel in portability and ease of storage, making them a great choice for those with limited space or who frequently travel.
- Technology Innovations: Inflatable boards benefit from the latest in fusion and drop stitch technologies, offering lighter, stronger boards that rival hard SUPs in performance.
- Choosing Your Board: Consider your paddling style, storage capabilities, and water conditions when selecting between a hard SUP and an inflatable paddle board.
Introduction

Embarking on your paddle board journey or leveling up your SUP skills? Let us help you understand the difference between the construction of hard and inflatable paddle boards.
Understanding Hard Board Construction

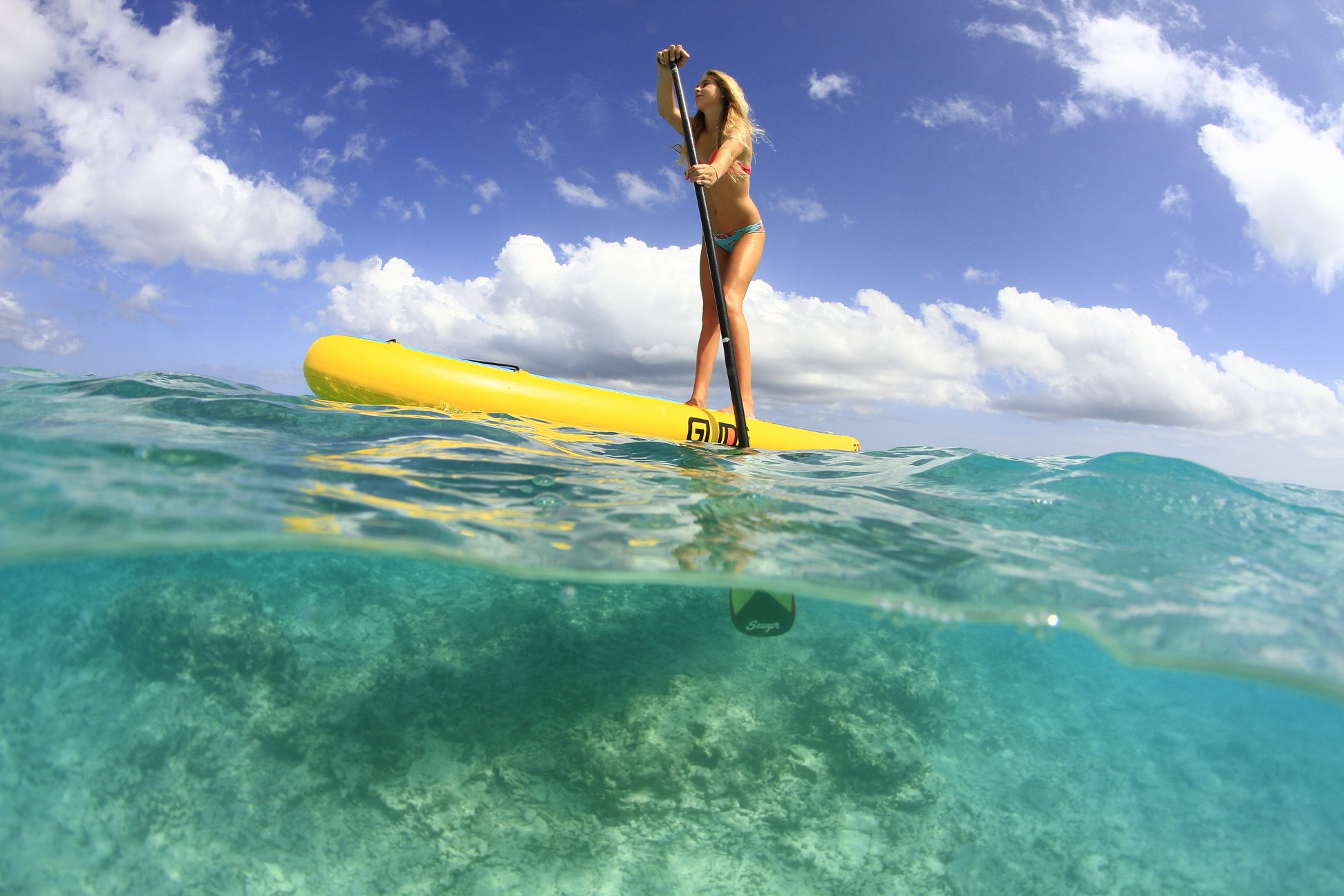
Much like surfboards, the original paddle boards were rigid boards. Most people are unaware of the various layers that go into a finely crafted stand up paddle board.
A paddle board starts out as a large block of EPS foam. Using a CDC machine that block is cut into 4 to 5 shapes that vaguely resemble solid boards. We call these shapes "blanks".
The SUP board blank is then "shaped". The shaping process involves using a an electric sander so that all of the edges of the board are rounded.
Once the board has been shaped, one side of it is covered with a large piece of fiberglass. Resin is then poured over the fiberglass and is spread out evenly using a squeegee.
After the resin dries for a day, the same process is applied to the other side of the board. An extra layer of fiberglass is usually added to the solid boards at this point to give it more strength.
Then a router is used to carve out spots for the fins and handle. Depending on the fin set up there might just be one fin box routed out or it could be three.
Once the epoxy has dried, it's time to lightly stand the board from top to bottom. Once completed, a hole for the leash can be drilled out. On the top of the board, it's time to drill out holes for the attachment points that bungess will be secured to.
Durable Hard Board Construction is Introduced

Glide's founder, Ken Driscoll set out on a quest to find a durable material that would let paddle boards absorb rock hits as he barrelled down rivers after breaking his back going of a 50-foot waterfall in a kayak and no longer being able to sit comfortably in a kayak cockpit. There was a lot of trial and error in those early days. Many paddle boards were broken along the way and the ones that didn't tended to weigh about 70 pounds.
The new ultra durable SUP boards became wildly popular with the whitewater SUP crowd. It wasn't long before companies that rented paddle boards were calling us to place orders.
The Technology Behind the Inflatable Paddle Board Revolution

In the realm of stand up paddle boarding (SUP), the evolution from rigid to inflatable SUP boards marked a significant leap forward. Initially, SUP enthusiasts were limited to hard boards, often cumbersome and challenging to store for those without ample space. The inception of inflatable paddle boards, inspired by the technology behind whitewater rafts, introduced a practical solution, offering portability without sacrificing performance.
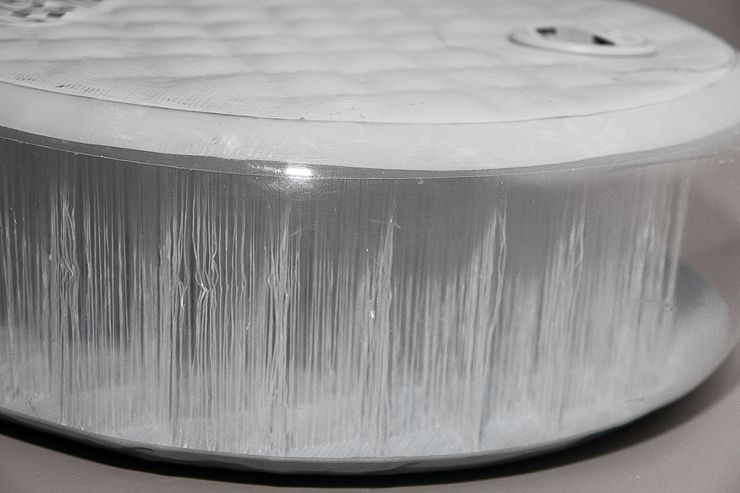
Inflatable SUPs are defined by their construction, primarily the use of PVC layers. High-quality boards utilize up to four layers of military-grade PVC, ensuring durability and resistance against wear. Traditional manufacturing methods relied on gluing these layers, leading to potential weaknesses and added weight. However, the advent of fusion technology allowed for the layers to be heat-fused, creating lighter, stronger boards with enhanced structural integrity.
At the core of inflatable SUP boards is the drop stitch technology. Contrary to the assumption that these boards are simply filled with air, they incorporate thousands of fine threads connecting the top and bottom surfaces. This design maintains the board's shape and rigidity when inflated. Two types of drop stitch exist: knitted and woven. Woven drop stitch, being the more advanced of the two, contributes to a sturdier board by employing a tighter weave that integrates strands at various angles for increased stability.
These technological advancements allow for a more rigid inflatable SUP when properly inflated, achieving higher board volume and performance levels. This rigidity also permits the board to support higher PSI levels, critical for ensuring the board's firmness and responsiveness in the water.
Rails on Inflatable Paddle Boards Should Not Be Dismissed
A lesser-discussed but crucial aspect of inflatable SUPs is the rail construction. The rail, or edge, of the board is pivotal, acting as the connection between the top and bottom layers. There are various rail types, with the Infla Rail system standing out for its single seam approach, significantly enhancing the board's integrity under high pressure.
In summary, the technology behind inflatable paddle boards encompasses innovations in materials, construction techniques, and design principles. These developments not only cater to the practical needs of storage and transportation but also ensure that enthusiasts enjoy a high-quality, durable, and reliable paddling experience.

Conclusion
Whether you gravitate towards the solid feel of a hard SUP or the versatility of an inflatable board, your choice reflects personal preference, lifestyle, and paddle boarding goals.